Nginx is a web server that can also be used as a reverse proxy, load balancer, mail proxy, and HTTP cache. Nginx could be used to create an API Gateway that processes requests in an event-driven manner, handling queries to the server in a quick, low-resource-footprint manner as they come in. Further, it reduces complexity and maximizes the performance by reducing the average response time to serve an API call.
Most of us are already familiar with Kong but, I wanted to explore the possibility of using OpenResty to build an API Gateway.
Implementation
For a personal website that's primarily content-focused, Astro was the perfect choice. It allowed me to deliver a fast experience without sacrificing the developer experience I love.
Design Philosophy
The first thing we need to do is to install OpenResty. OpenResty gives us the capability of scripting Nginx using Lua.
Once installed, you should navigate to your browser and type http://localhost. If everything goes well, you will see the below screenshot:
If you see the default Nginx welcome page, congratulations! You've successfully installed OpenResty.
Now, we need to edit the nginx.conf file. You can find the nginx.conf file in the below locations:
- Ubuntu: /usr/local/openresty/nginx/conf
- Mac: /usr/local/Cellar/openresty/nginx/conf (with Homebrew)
Note: You can also add the configuration in a new file and include it in nginx.conf.
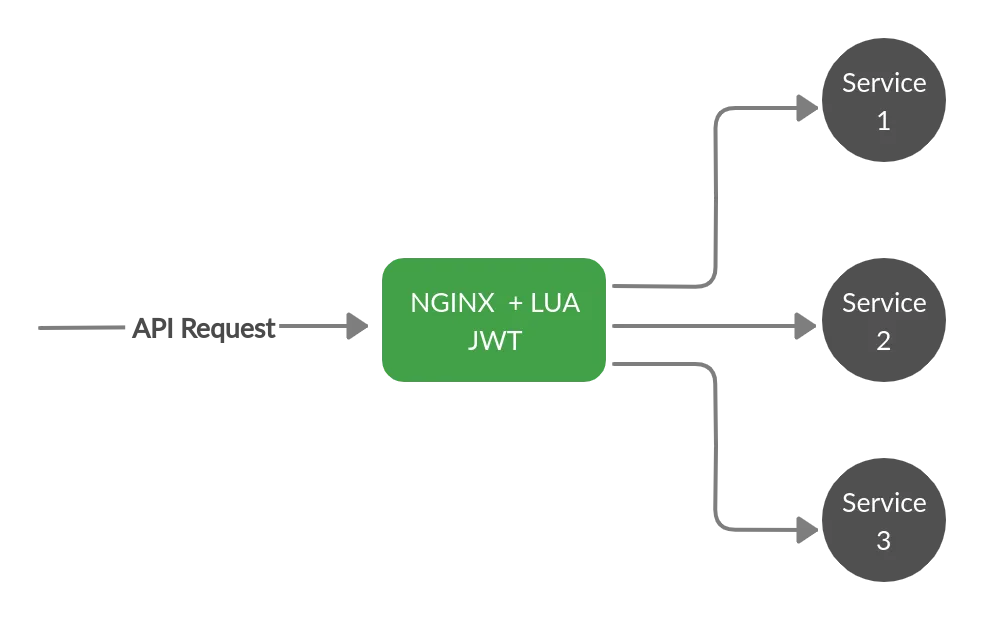
- Routing
- Authentication
Routing
To route the endpoints to their respective servers, all you need to do is:
location /api {
proxy_pass http://backend-api;
}Authentication
To perform authentication, I will be using JWT. To do that, we need to install the lua-resty-jwt library using OPM(OpenResty Package Manager).
opm get SkyLothar/lua-resty-jwtlocal jwt = require "resty.jwt"
local validators = require "resty.jwt-validators"
if ngx.var.request_method ~= "OPTIONS" and not string.match(ngx.var.uri, "login") then
local jwtToken = ngx.var.http_Authorization
if jwtToken == nil then
ngx.status = ngx.HTTP_UNAUTHORIZED
ngx.header.content_type = "application/json; charset=utf-8"
ngx.say("{"error": "Forbidden"}")
ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_UNAUTHORIZED)
end
local claim_spec = {
exp = validators.is_not_expired() -- To check expiry
}
local jwt_obj = jwt:verify('secret', jwtToken, claim_spec)
if not jwt_obj["verified"] then
ngx.status = ngx.HTTP_UNAUTHORIZED
ngx.header.content_type = "application/json; charset=utf-8"
ngx.say("{"error": "INVALID_JWT"}")
ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_UNAUTHORIZED)
end
endThe above Lua code does the following:
- It forwards the request to the next line of execution if it is an OPTIONS call or a login API.
- Otherwise, it fetches the JWT token in the Authorization header. If the token is not present, the code returns 'FORBIDDEN'.
- This JWT token is then validated for authenticity and expiry date.
- Once the token is validated, it forwards the request to the respective service. Else, it returns 'INVALID_JWT'.
Testing
To check the changes we have made, restart OpenResty using the below command
sudo service openresty restartOnce you restart, hit the API using Postman or any other REST client and validate the response.
Tip: You can generate JWT tokens using this website: http://jwtbuilder.jamiekurtz.com/
Todo
We can improve our auth script by doing the following:
- A mechanism to add new API endpoints that don't need a JWT token like downloads API.
- Currently, JWT secret token is hardcoded in the script. Maybe we could set it as an environment variable to make it dynamic.